UV Technology in Hot Water Sanitation
Waterborne pathogens in domestic and commercial hot water systems pose significant health risks, particularly in healthcare facilities, hotels, and residential properties. Traditional thermal disinfection methods require heating water to high temperatures, consuming substantial energy and increasing operational costs. Modern UV hot water sanitation offers a chemical-free, energy-efficient alternative that destroys harmful bacteria without altering water quality or taste. Heating and Plumbing World provides expert guidance on integrating UV technology into existing heating systems.
What Is UV Hot Water Sanitation?
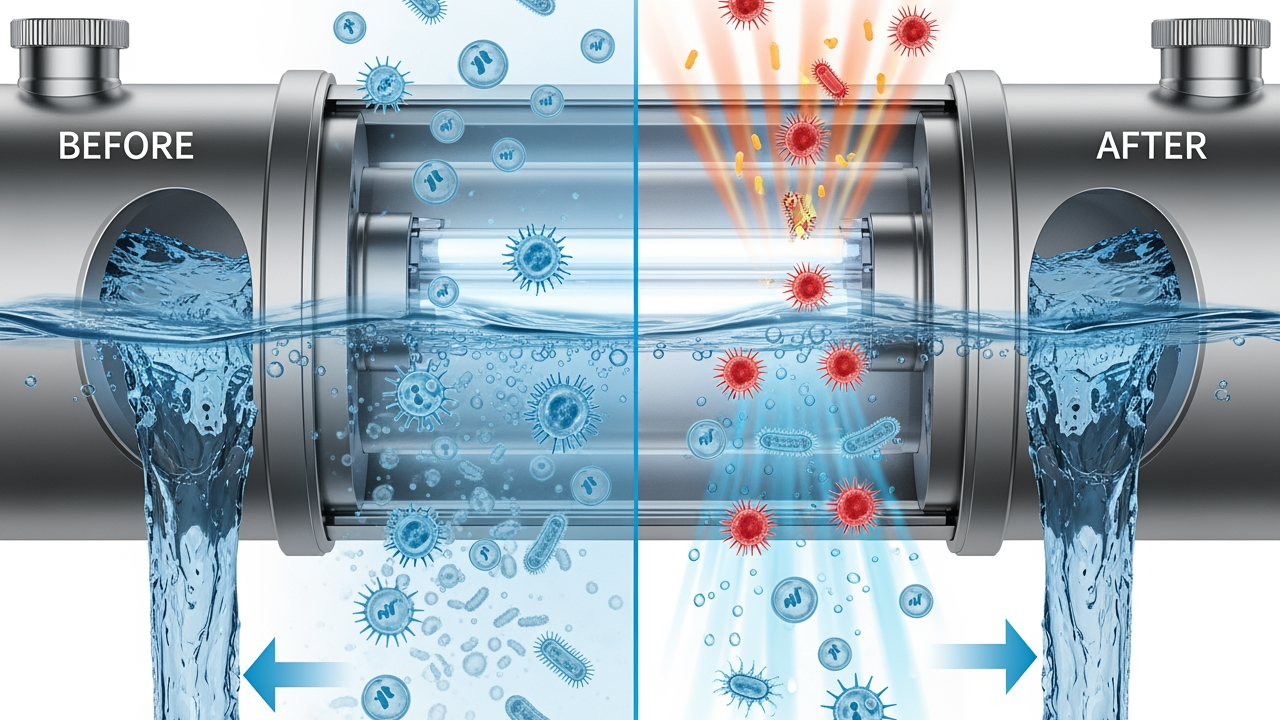
UV hot water sanitation uses ultraviolet light at specific wavelengths to eliminate bacteria, viruses, and other microorganisms in water systems. The process relies on UV-C light, which operates at wavelengths between 200 and 280 nanometres. This germicidal wavelength penetrates the cell walls of pathogens, disrupting their DNA structure and preventing reproduction. Unlike chemical treatments, UV sterilisation leaves no residual taste or harmful byproducts in the water supply.
A UV-based water steriliser typically consists of a stainless steel chamber housing a UV lamp protected by a quartz sleeve. Water flows through the chamber, exposing pathogens to UV-C radiation for sufficient contact time to achieve effective sterilisation. The quartz sleeve remains transparent to UV light while protecting the lamp from direct water contact and temperature fluctuations.
How UV-Based Water Sterilisers Work
The sterilisation process begins when water enters the UV chamber at a controlled flow rate. The UV lamp emits germicidal radiation that passes through the quartz sleeve and penetrates the flowing water. Microorganisms absorb this UV energy, which damages their genetic material and renders them unable to reproduce or cause infection.
Contact time - the duration water remains exposed to UV light - determines sterilisation effectiveness. Systems must balance flow rate against lamp intensity to ensure adequate exposure. Most residential UV-based water sterilisers operate at flow rates between 10-40 litres per minute, whilst commercial systems handle significantly higher volumes.
Modern systems include monitoring features that alert users when lamp intensity decreases or requires replacement. Safety interlocks prevent water flow when the UV lamp malfunctions, ensuring consistent water quality. Integration with existing boiler spares and heating components allows seamless installation in both new and retrofit applications.
Benefits of UV Technology for Hot Water Systems
Health and Safety Advantages
UV hot water sanitation eliminates up to 99.99% of bacteria, including Legionella pneumophila, without introducing chemicals into the water supply. Healthcare facilities particularly benefit from this technology, as immunocompromised patients face heightened risks from waterborne pathogens. The chemical-free approach means no chlorine taste, no disinfection byproducts, and no handling or storage of hazardous chemicals.
Unlike thermal disinfection that requires heating water to 60°C or higher, UV sterilisation works effectively at normal hot water temperatures between 50-55°C. This reduces scalding risks whilst maintaining comfort and safety. The technology also proves effective against chlorine-resistant organisms that survive traditional chemical treatment.
Efficiency and Environmental Benefits
Energy consumption decreases significantly compared to thermal pasteurization systems. A typical UV-based water steriliser consumes 40-150 watts, equivalent to a standard light bulb, whilst thermal systems require substantial energy to heat entire water volumes to lethal temperatures for pathogens. This efficiency translates to reduced carbon emissions and lower utility bills.
The technology requires no consumable chemicals, eliminating recurring purchase costs and environmental impacts associated with chemical production and disposal. Systems integrate easily with expansion vessels and other water system components without requiring extensive modifications.
Applications in Domestic and Commercial Settings
Residential properties benefit from UV hot water sanitation in areas with well water supplies or where municipal water quality raises concerns. Homeowners installing the technology alongside quality water tanks ensure comprehensive water safety throughout their property.
Hospitals and healthcare facilities represent the largest commercial application sector. Patient safety demands reliable water sterilisation, particularly in critical areas like burn units, transplant wards, and neonatal departments. UV systems provide continuous protection without the maintenance demands of thermal disinfection loops.
Hotels and hospitality venues face strict water quality regulations whilst managing high water consumption volumes. UV technology meets these demands efficiently, protecting guests from waterborne illness whilst controlling operational costs. Food preparation areas, where water quality directly impacts food safety, also benefit significantly from UV sterilisation.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Professional Installation Considerations
Proper system sizing requires professional assessment of water flow rates, peak demand periods, and specific pathogen concerns. Engineers must position the UV chamber to ensure adequate space for lamp replacement and maintenance access. The system typically installs on the outlet side of water heaters or storage tanks, treating water immediately before distribution.
Integration with existing heating systems requires consideration of pressure, temperature, and flow characteristics. The technology works effectively with oil boilers, gas boilers, and thermal stores. Professional installers ensure proper electrical connections, as UV lamps require dedicated power supplies with appropriate circuit protection.
Ongoing Maintenance
UV lamp intensity decreases over time, typically requiring replacement every 9-12 months regardless of whether the lamp appears to function. Manufacturers provide specific replacement schedules based on operating hours and system design. Some advanced systems include lamp life monitors that track cumulative operating time and alert users when replacement becomes necessary.
The quartz sleeve requires periodic cleaning to remove mineral deposits and biofilm that reduce UV transmission. Cleaning frequency depends on water hardness and quality, ranging from quarterly to annually. Most systems allow quartz sleeve removal without disrupting the water supply, minimising maintenance downtime.
Regular inspection of pressure relief valves and other safety components ensures system integrity. Annual professional servicing includes lamp intensity testing, quartz sleeve inspection, and verification of proper water flow rates through the UV chamber.
Comparing UV Sanitation to Traditional Methods
Chlorination remains common in municipal water treatment but requires careful chemical handling and creates potential disinfection byproducts. UV hot water sanitation eliminates these concerns whilst providing comparable or superior pathogen destruction rates. However, UV technology lacks residual disinfection capability - it only treats water passing through the chamber, whilst chlorine maintains antimicrobial activity throughout distribution systems.
Thermal pasteurization effectively eliminates pathogens but demands continuous energy input to maintain lethal temperatures. A UV-based water steriliser achieves similar results with fraction of the energy consumption. Thermal methods also accelerate scale formation in heating systems and increase wear on components, whilst UV technology imposes no thermal stress.
Cost analysis reveals UV systems typically recover initial investment within 2-4 years through energy savings and reduced chemical costs. Systems demonstrate particular value in properties with high hot water demand or where energy costs remain elevated. The technology pairs well with modern condensing boilers and heat pumps that benefit from lower operating temperatures.
Conclusion
UV technology transforms hot water sanitation by providing chemical-free, energy-efficient pathogen control for residential and commercial applications. The combination of proven effectiveness against dangerous bacteria, reduced operational costs, and minimal environmental impact makes UV-based water sterilisers an increasingly popular choice for property owners and facility managers. Modern systems integrate seamlessly with existing heating infrastructure whilst delivering reliable water quality protection.
Whether upgrading an existing hot water system or designing a new installation, UV hot water sanitation deserves serious consideration. The technology offers particular advantages for healthcare facilities, hospitality venues, and any property where water quality directly impacts health and safety. To explore how UV sterilisation can enhance your water system's performance and safety, contact us for expert consultation and professional installation services.

 -
-